Advertisements
Special Types of Disk Drive
Supper floppies -- Zip drives, LS120, HiFD
- Rapid growth in HDD & slow growth in FDD
- Cheap
- Good for back up
- Portable PC card version available
Zip drive (Bernoulli’s box) – Inventor – Iomega
- Similar to floppy but use zip cartridge for media
- Twice thicker than floppy disk
- Size: 4 inch square
- Capacity: 100MB & 250 MB
- Variable sectors/track – max usable disk space
- Better reliability & portability
- Used for OS installation without CD/Several floppy
- Can be internal or external drive
Type of Interfacing
Ls 120
- 120MB std aims to replace regular fdd
- Can read 31/2” floppy faster
- SCSI version of ZIP faster than LS120 drive
Hifd (high floppy disk – sony’s)
- Capacity of 200MB on 31/2” floppy disk
- Can read & write old & new floppy disk
- Faster than LS120 drives
Mo drives (magnetic optic drives)
- Magnetic medium
- Laser beam-laser guided magnet heats very minute area 300o C
- During Read, Laser beam detects polarization of micro magnets
- Fast
- Extremely stable
- Wear Proof
- Data Life Span: 30years
- Popular: Sony’s Recordable Mini Disc
MODEM
- MODulator Cum DEModulator
- I/O device to link computer to telephone line to communicate with another computer
- Transmits voice and data as analog signals
- Transmits digital data into analog voltages & transmit over telephone line
- Receiving end – another modem converts analog to digital data
- Now, a house hold device

Fax modem
- Modem with additional capability of sending & receiving faxes
- Fax- s/w transmits document in a system
- Files can be printed if needed
Cd rom drive (Compact disk read only memory)
- Read only device – large capacity – low cost
- Essential in multimedia system
- Highly reliable
- Uses optical technology
- Storage capacity: 680Mb – Larger
- Speed: HDD > CD Drive > FDD
Storing Information
- Laser beam used for storing information
- Data on CD is stored on single continuous spiral track from centre of length is 5Km & 650Mb that is divided into sector
- Track Density – very high
- Gap between tracks is 1.6 microns
- Data bits – represented by “pit” (1) & “land” (0)
- Land reflects & Pit does not reflect
- While recording a laser burns spots on disk forming pits & lands
- During reading, laser beam is focused on the track
- Light reflected from Land > Pit
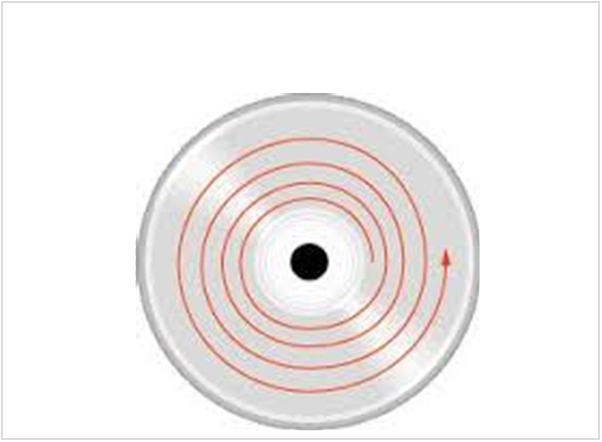
Cross section of a CD media
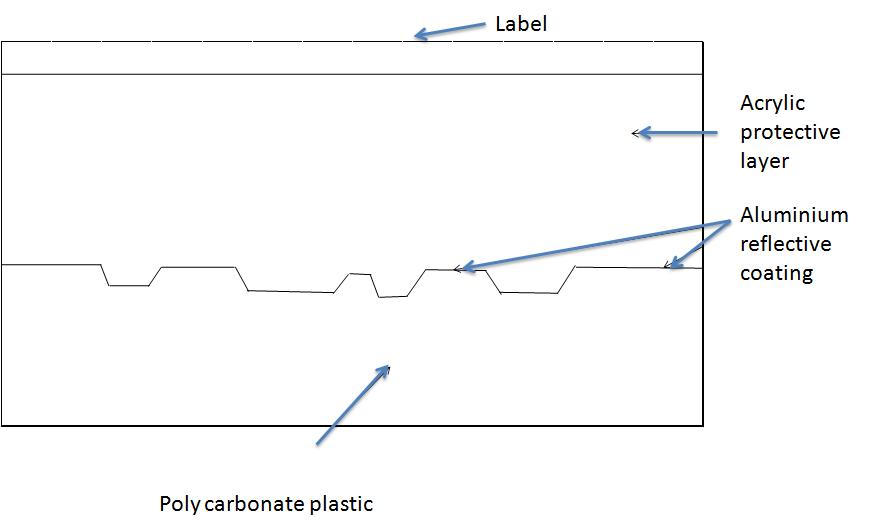
Sectors
- CD is made of reflective material encased in plastic layer
- Each sector stores 2048 bytes of data
- In each sector a 12 byte sync field & 4 byte header field
- Sector address format – mins:Secs:Sector
- First sector – 00:00:00
- Second sector – 00:00:01
- 1st three sectors – reserved & no user data
- Equal length for all sectors
CD-ROM drive operation
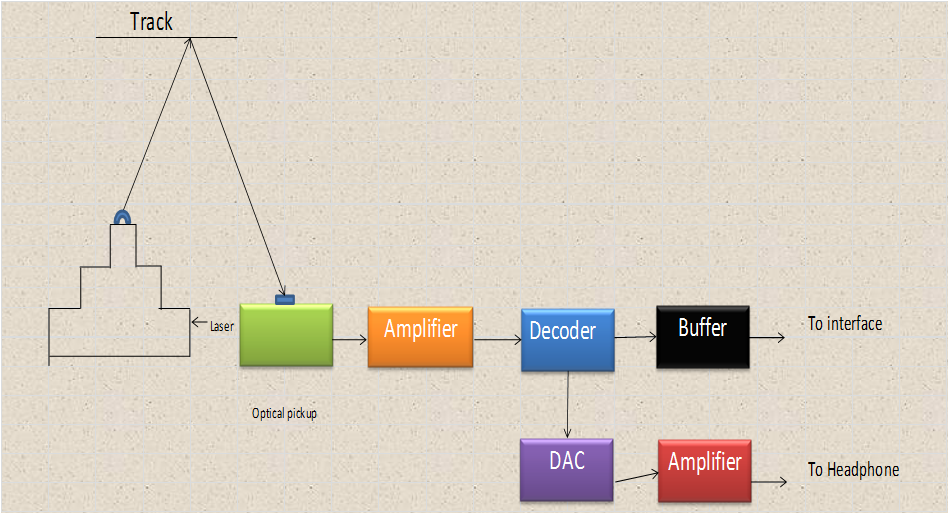
- Constantly changing rotational speed
- Linear Velocity (CLV): On reading outer area, single speed CD ROM Drive spins at 200rpm & on reading inner area – 530 rpm
- CD-ROM drives spin faster than CD players
- CD’s Data transfer is 150 Kb/Sec
- CD-ROM’s speed is specified as multiple of data transfer rate of CD – 1x, 2x, 4x, 36x, 48x, etc
Advantages of CD ROM drives
- Both readable & Writable CD available
- Essential for multimedia application
- Distribution medium by software suppliers
- Not Sensitive to dust, scratch, magnetic fields & temperature variation
- Large capacity & High reliability
CD-R Drive (Compact Disk – Recordable) (Burner)
- It has once only writable capability
- Uses: To distribute s/w, S/w backup, File archiving
- A Preformed raised grove is present
- Pits are burnt on groove by firing laser on hot layer organic dye
- Can read from CD – R
- Std Capacity: 628MB & 737MB
CD – RW Drive (Compact Disk – Rewritable)
- Can read & write
- Re-burning of 1000 times is possible
- Phase-change alloy forms recording layer
- Over writing data is done with 2 different temperature & laser beam alternating between them
Scanner
- Input device to convert pictures & text into stream of data
Types
1. Drum scanner
- High quality & price
- High sensitivity & good signal – to – noise ratio
- Photo Multiplier (PM) tube – light sensing
- Image – spinning drum (captures shadow info) – transform to visible region
2. Flatbed scanner
- Material kept on flat bed of glass
- Light source & CCD (Charge coupled device) mounted on carriage
- CCD – converts light to electric pulses
- Scanning head (with CCD) moves across pictures

3. Sheetfed scanner
- Paper is pulled over scan head
- Small Size
- Improper Mechanism can skew the paper
4. Hand held scanner
- Held in hand and moved over document sliding over it
- Low cost
- Portability
- Poor quality


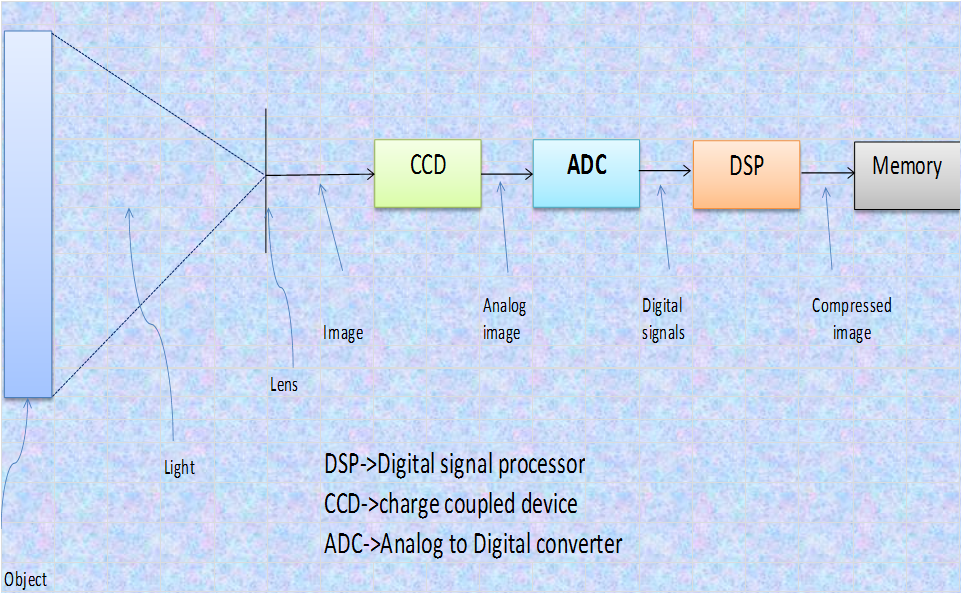
Digital camera

- Captures instant digital images on internal memory/floppy – interface to PC – transfers to hard disk
- Lens – focus image
- CCD – primary sensing
- CCD array of tiny photo transistors arranged in grid
Block diagram of a digital camera
DVD (digital versatile disk)
- Storage capacity 17 GB
- Uses MPEG & Dolby compression tech – ideal multimedia peripheral device
- High quality video & audio
- Distance between track – less than half that in CD
- Pits – smaller than in CD
- Laser spots ‘ve to be smaller – reduced wavelength.
