Advertisements
Special Peripherals
Application
- CAD (Computer Aided Design)
- CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing)
- DTP (Desktop Publishing)
Plotters
Graphics output device to create drawings on paper
1. Pen Plotter
- Electromechanical device
- Moved in two dimension across paper/film media
- Ink pens & Multiple color pens are used
Types of Pen Plotters
- Drum Plotter – Drum rotates & Pen carriage moves horizontally
- Microgrip Plotter – Medium gripped at edges–moved to & fro
- Flatbed Plotter – Pen carriage moved along X & Y axis in short digital steps using stepper motor
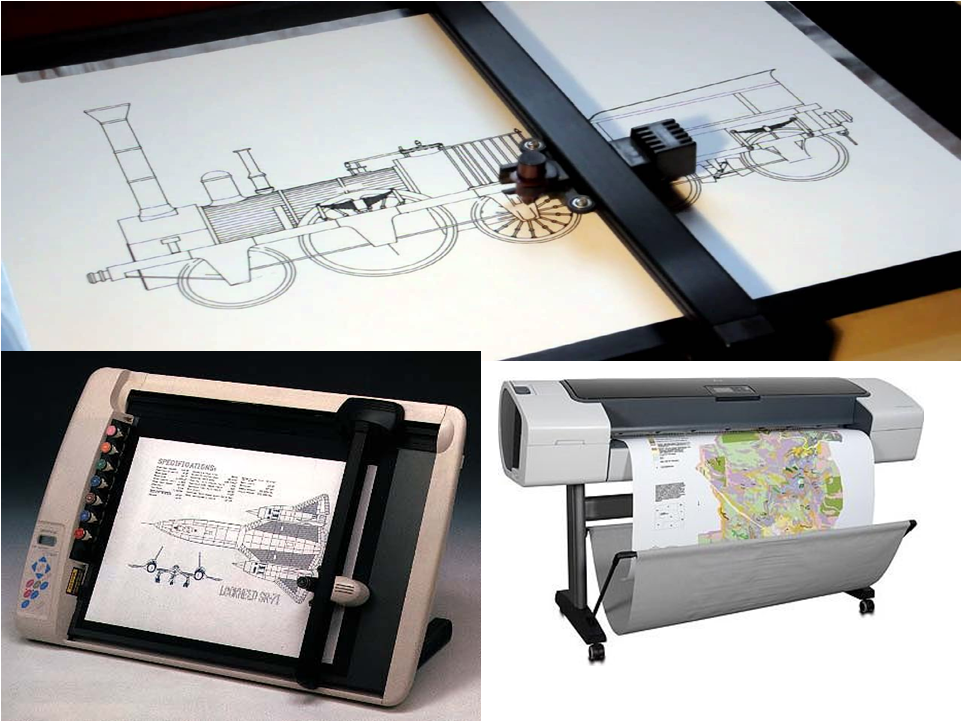
2. Photo Plotter
- Uses fiber optics tech
- Produce image on dry silver paper
- Size: A4, A3, etc
- Expensive
- Excellent Quality
- Can prepare quick & beautiful engineering drawings
- Can be interfaced to computer via serial & parallel interface

Light pen
- I/p device in CAD application that can indicate current active position to 1 program
- Photo sensor detects presence of light – connected via cable to computer
- When tip of light pen touches a spot on CRT,light pen is activated
- Light is sensed & signal is sent to micro computer
- Computer notes the position of spot where light pen is touched

Joystick
- High accuracy not needed & used in simple application
- Used in playing games for creation of general symbol shapes
- A Lever protrudes through top of unit & can be tilted at different angles
- Joy stick can control cursor on CRT screen – visual indication to user
- Rate of speed of cursor is directly propositional to distance of joystick lever from vertical position

Digitiser or graphic tablet
- Has flat surface like drawing pad & pointing device
- X-Y line co ordinate system converts rough sketch to fine drawing by transferring point & line location to computer
- Pointing devices: Stylus/Pen, Push button cursor/Puck, Power module or console menu
- Grid platter of horizontal & vertical line below flat surface of digitiser detects electrical pulses at X-Y coordinate
- Popular i/p device in CAD
- Available in many sizes
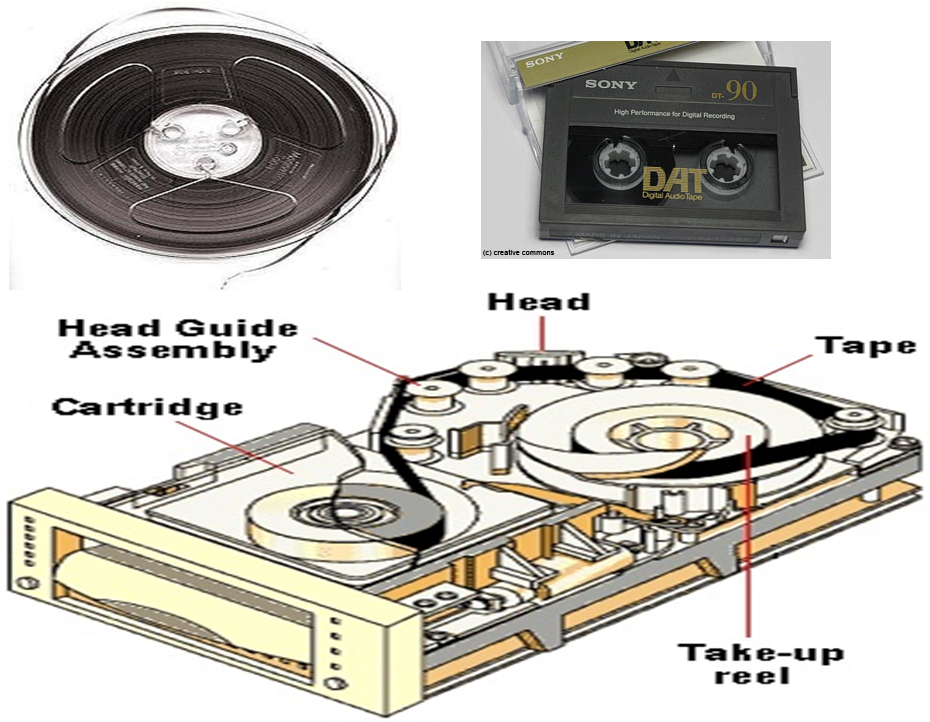
Magnetic tape drives (Start / stop drives)
- Oldest device for storage by older main frames & mini computer
- Tape spool of 2400 feet – easy & convenient to transport files to store data & even OS
- It has 9 tracks across length – 8 bits off data & 1 parity bit – CRCC
- For each track, tape drives had 9 set of heads, each having Erase, Write & Read heads
- Head assembly – fixed & tape media moved
- Positioning mechanism: Vacuum Column or Tension arm System
- Recording Tech NRZI (Non return to zero Inverted)
- Important back up device during data loss
- Tape housed in cartridge. (Quarter inch Cartridge)
| Tape Drive | Capacity | No of tracks | Interface | Transfer speed | Remarks |
| Quater inch catridge(QIC) | 40 MB-13 GB | 9 to 144 | QIC/SCSI-2/Parallel port | 12 MB/min - 18 MB/min | Ideal for servers |
| Full size QIC Mini Catridge | 40 MB- 13 GB | 20 to 144 | Floppy/IDE/SCSI/QIC | 2 MB/Min - 9 MB/Min | Smaller size; Ideal for PCs |
| Travan tape | 40 MB - 4GB | 36 to 72 | Floppy/EIDE/SCSI | 62.5KB/sec - 567 KB/sec | Higher density |
| Helican scan tape: 4mm digital audio tape(DAT) & 8 mm | 2 GB - 4 GB | Full surface | EIDE/SCSI | Full tape surface used |
QIC drive
- Faster tape than casette tape
- Holds 300 or 600 feet of tape
- Mini cartridge holds 62.48-m (205’) quarter-inch tape
- Uses MFM or Run Length Limited (RLL) (s/w cares it)
- High recording density – Travan Tape Cartridge drive
Helical – Scan tape drive
-
R/W heads mounted on drum
-
Rotation – 2000 RPM
-
Tape wraps about 90o around drum’s circumference
-
Slight angle between tape’s path & drum
-
Helical span path formed by moving drum on moving tape
-
Complete surface of tape is used
Backup
- Slower tape drives. So longer time for back up
- Server uses RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Drives) with multiple disk drives
- Cost is higher – worth for critical server data
