Advertisements
Printer
- Electromechanical device
- Computer interface – links computer & printer – commands & data, Printer Status
- Printer Electronics – decode command, generate control signals, activate print mechanism
Mechanical assemblies – print assembly, paper movement assembly & sensor assembly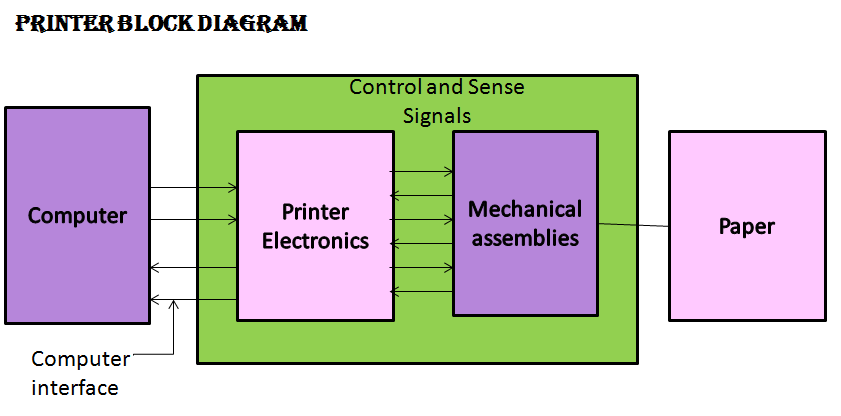
Printer Functions
- Receives printable data char & non-printable control char
Control characters:
|
Symbol
|
Control Characters |
Function |
|
CR |
Carriage Return |
Return to 1st column |
|
LF |
Line Feed |
Skip one line |
|
FF |
Form Feed |
Skip paper to beginning of next page |
Each page – form.
|
Character |
Indicates |
Specified as |
|
SPEED |
How fast a printer works |
CPS – Characters per second, LPM – Lines per min, PPM – Pages per min |
|
QUALITY |
How good the shape of printed character is |
DRAFT, NQL – Near Letter Quality LQP – Letter Quality Printer |
|
CHARACTER SET |
Total no. of data characters & control characters |
|
|
INTERFACE |
Parallel form / Serial form |
|
|
BUFFER SIZE |
Data char in buffer memory |
|
|
PRINT MECHANISM |
Dot matrix, daisy wheel, golfball, thermal, band, belt, drum train, chain, inkjet, laser. |
|
|
PRINT MODE |
Serial/ Parallel |
|
|
PRINT SIZE |
Character size, No. of char per line |
|
|
PRINT DIRECTION |
Unidirectional, Bidirectional, reverse, logic seeking |
Common forms of paper
- Single sheets
- Fan fold
- Roll
Paper Movement
- Friction feed
- Tractor feed
- Pin feed
- Sheet feed
Modules inside a printer
- Print-head Mechanism
- Carriage Movement
- Paper feed
- Control electronics
- Interface logic
- Power Supply
Printer Types
1.Based on printing technique
1. Impact printer
- Character formed by physical contact of print head on ink ribbon/ paper
- Eg: Dot matrix printer, Daisy Wheel, Golf ball, Drum, band, Chain
2. Non- impact printer
- No physical contact of head with paper or ribbon
- Eg: Laser printer, thermal, inkjet & electrostatic printer.
2. Based on Printing sequence
1. Character printer (Serial Printer)
- Characters printed one after the other
- i.e., one character at a time
- E.g: Daisy wheel printer, Dot matrix printer.
2. Line Printer (Parallel Printer)
- Prints a complete line (many characters) in one shot
- Eg: Drum printer, band, chain printer
- High speed & specified in CPS, LPM or PPM
3. Based on Print Quality
1. Draft Printer
- Print character is formed by closely spaced dots
- Visible but not impressive
- Eg: Dotmatrix printer
2. LQP (Letter Quality Printer)
- Whole char is formed as letter (|||r to type writer)
- Pleasant to read, used in office
- Eg: Daisy wheel printer
3. NQL (Near Letter Quality Printer)
- Prints char as pattern of dots & prints twice – Offset
- More Impressive
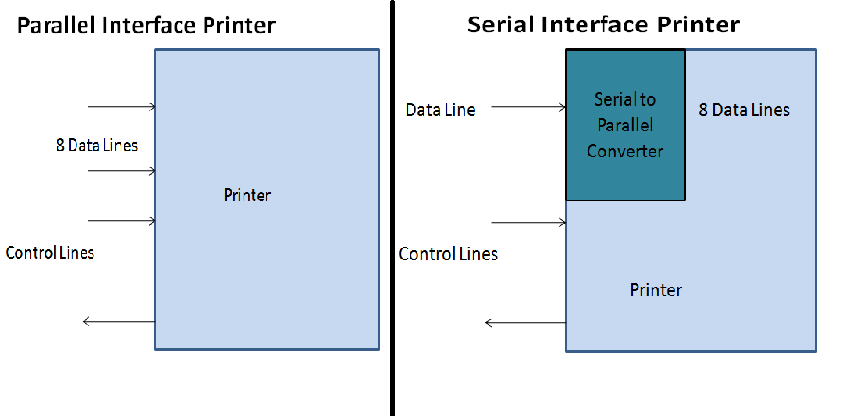
4. Based on Print Interface
1. Parallel Interface Printer
Eg: Centronics with 36 pins
2. Serial Interface Printer
Eg: RS 232 C
5. Based on Print Direction
1. Unidirectional Printer
- Print head moves in only one direction (left to right)
- |||r to manual typewriter
2. Bidirectional Printer
- Printing is performed during both direction of head movement (left to right & right to left)
3. Reverse Printer
6. Based on Printing sequence
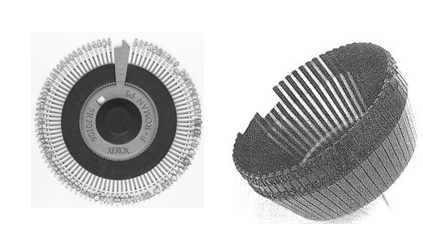
1. Daisy Wheel Printer
-
Print head has circular wheel with 96 spokes/character
-
Each spoke has a raised char embossed at tip
Working
- Rotate wheel till desired char is on paper
- Solenoid driven hammer strikes petal & ribbon & paper
- Move print head to next column
Pros: Good quality print
Easy Font interchange
Speed: 10 – 60 CPS Eg: QUALTERM 45/55 & DATA TERMINALS 302
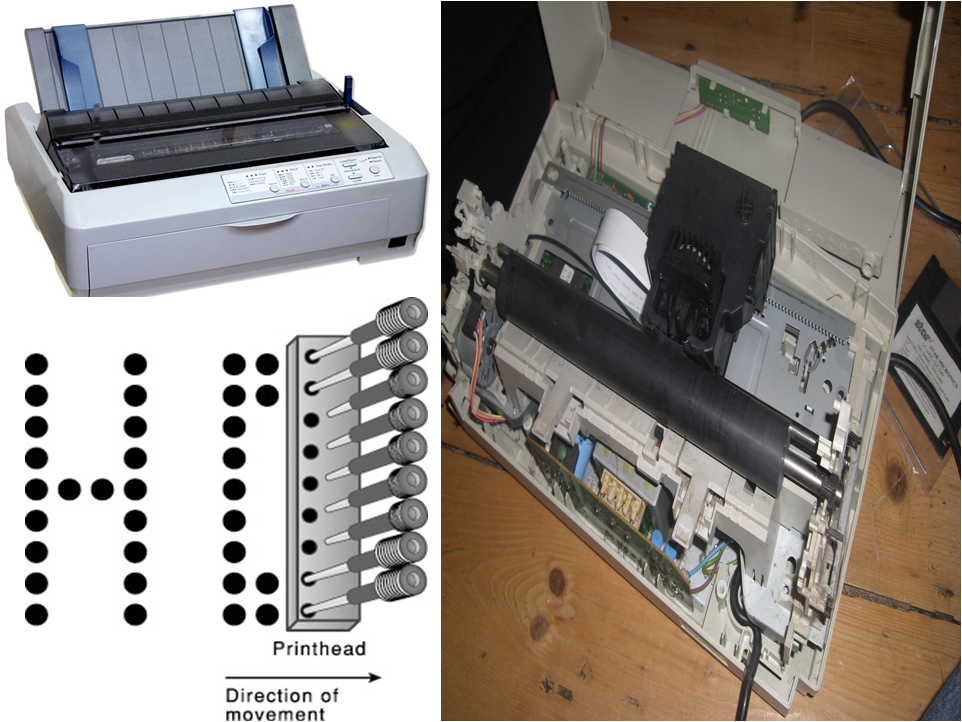
2. Dot Matrix Impact Printer
-
Character – dots using 7 by 5 matrix pattern of dots
-
Print head – pins & solenoid
- Head moves column by column to print a character
- Quality is _______________
- By using greater number of pins or printing twice with a sight offset for dots _______ is achieved
Advantages
- Print graphics – sequential dots
- Print in any language, no hardware change
- Colour printing by colour ribbons
- Lower price
Speed
- Draft mode – 100 to 300 cps
- NQL mode – 25 to 50 cps
Eg
- WIPRO FX 105, CENTRONICS 702, DATA PRODUCTS M 200, DIABLO SYSTEMS 2300, HP 2635 A
Golf – Ball Printer
-
Characters embossed in spherical golf-ball metallic unit
-
Drive mechanism moves the ball to print desired character
- Ball is pushed over ribbon to print leter on paper
Adv:
- Excellent Print quality
- Font can easily be changed by changing the ball
Speed:
- less – 10 to 15 CPS

Thermal Printer
- Special heat sensitive paper
- Print head – heating elements
- Char printed as matrix of dots
- On switching ON heating element, spot on paper heated & turns dark – creates letter.
- Also, normal paper but heat sensitive ribbon
- Consistent print quality
- High Running cost due to special paper/ribbon

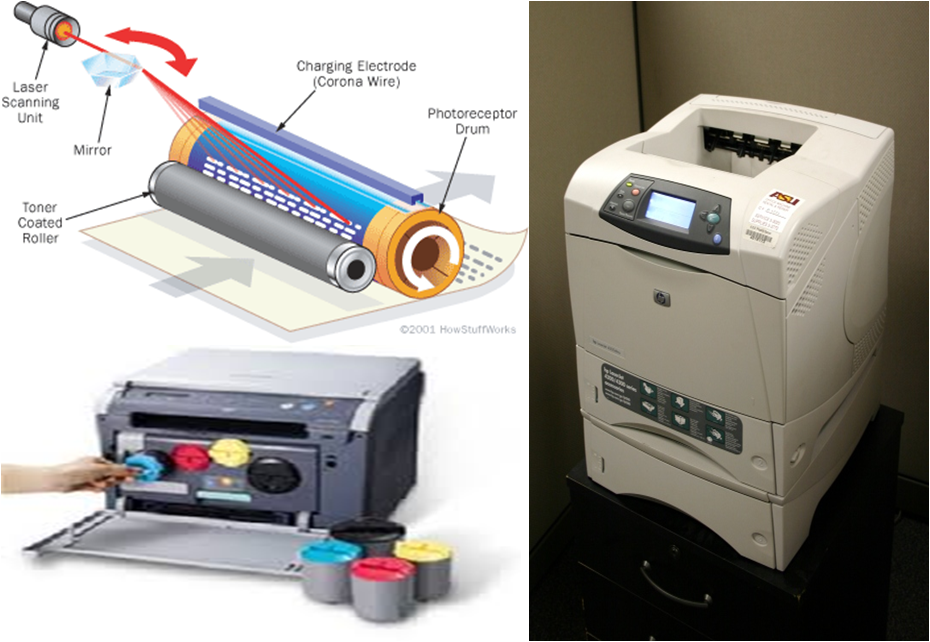
Laser Printer
- |||r to xerox machine
- Laser creates image on photosensitive drum
- Laser turned ON & OFF – sweeps back & forth across the drum
- Image inked by applying toner on drum. Electrostatically transferred from drum to paper
- Popular – Hewlett-Packard Laser jet
- High Letter quality & Speed
- High Price

LED Printer
- Instead of Laser Light emitting Diodes (LEDs) used to expose from drum
- No moving parts
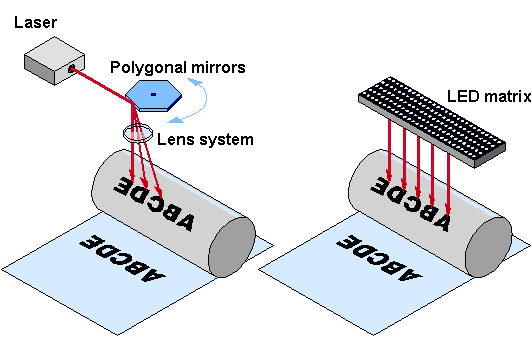
Ink Jet Printer
- Better Quality printout
- Very sharp output
- Cheaper
- Colour print
- No pins or ribbon / matrix of dots
- Tiny dots of ink is sprayed onto paper
- When print head moves across paper, jets spray ink to form letters
- has 48 to 128 pins
- Print quality – Dots per inch (dpi)
- Deskjet & Bubblejet are standard Ink jets
- Eg: Hawlett- Packard, Canon, Epson & Lexmark
