Advertisements
Personal computer concepts
Benefits of Microcomputer:
- Low cost (computer cost + installation + maintenance)
- Small size, low weight & low power
- No need for air conditioning
- Design & packaging of PC is simple
- User can handle installation
Microprocessor(μP) as a CPU
- μP - CPU on single IC
- Building Computer is simplified.
- To handle variety of peripheral device - more powerful PC
- Special purpose ICs like interrupt controller, DMA controller, interval timer, etc are included as support chips to μP .
- Recently, special chip-set provides the functions of all support chips.
Bus Concept
During execution of a program in a computer, information flows from one unit to other.
Types of Information
- Instruction
- Memory Address
- Data
- Register Address
- Control Signals
- Input/Output command
- Input / Output device address
To the central units (CPU, Memory & DMA Controller) other peripheral subsystems (i/o controllers) are interfaced.
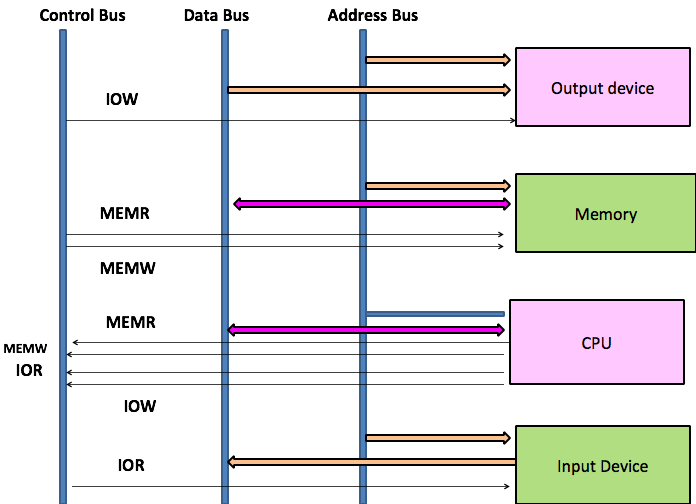
Types of Information between CPU & Memory:
1. Memory Address
i. During instruction fetch, contents of Program Counter are sent to MAR in memory
ii. During operand fetch, contents of register in CPU are sent to MAR.
2. Memory Data
i. During instruction fetch, contents of MDR are sent to IR in CPU.
ii. During operand fetch, contents of MDR are sent to register in CPU. Communication between the units incorporating the bus concepts are divided into Data, Address and Control.
Multiple paths – high cost of hardware
3. Types
Data Address Control
Data – Instruction & data
Address – Memory address/ Peripheral address
Control – control signals like mem read/write, I/O read/write, interrupt, reset.
When used?
Data
Control
Address
Bus Arbitration
CPU (Bus master) decides who should control the bus when more than one unit wants bus at same time.
Only CPU & DMA controller controls the bus
Any unit can make bus request & waits for CPU to sanction it.
BUS Concept
Bidirectional Bus
Categories of signals on the bus
- O/P signals from microprocessor
- I/P signals to microprocessor
- Signals both o/p from & i/p to microprocessor
Operand Store
- μP puts mem address from internal register on to address bus
- μP puts data from one of internal registers onto data bus
- μP issues Memory write signal on control bus
- Memory takes contents on data bus & stores in given location
Data Bus
- Bidirection (from μP to memory & from memory to μP) – internal mechanism
- I/p & O/P to CPU & Memory
Address bus
- Uni directional (from μP to memory)
- CPU never receives info from address bus
- Only in built-in cache – bidirectional to support cache invalidation.
- Data cant be sent
Control bus
- Collection of control signals generated by & sent to μP
- 11 Control signals
To remember:
- i/p or o/p from or to μP
- Task it does
- DMA involved or not?
Control Bus Signals
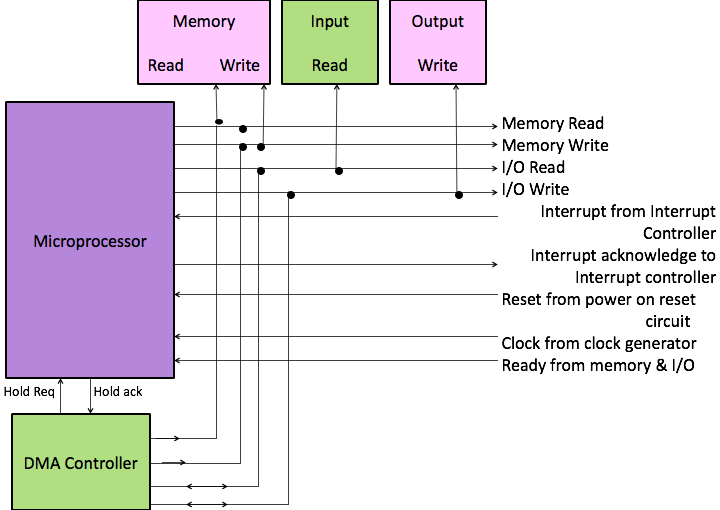
- Memory Read
- Memory Write
- I/O Read
- I/O write
- Interrupt
- Interrupt Acknowledge
- Hold Request
- Hold Acknowledgement
- Reset
- Clock
- Ready
Demultiplexing Bus
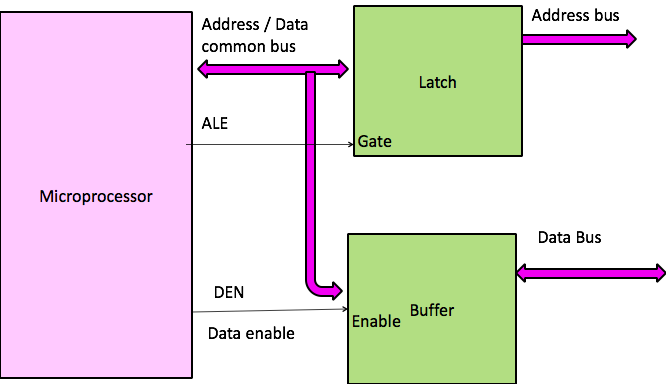
Multipurpose micro processor
Objectives
- Reduction of hardware circuits
- Exploitation of μP for better utilization
- Design flexibility, Open to modifications
Extra Functions:
- Self Test
- POST – Power-On Self-Test – execute as soon as PC is powered on
- Verifies hardware fault
- On error – PC halts with error message/code/abnormal symptom
- POST routines are stored in ROM
- Bootstrap Program
- IPL – Initial Program Load
- by firmware on ROM
- POST Program Pass control to bootstrap
- Initialization of Programmable LSI
- Parameters to LSI
- mode of operation desired
- command to be executed
Interface to Operating System & IOCS
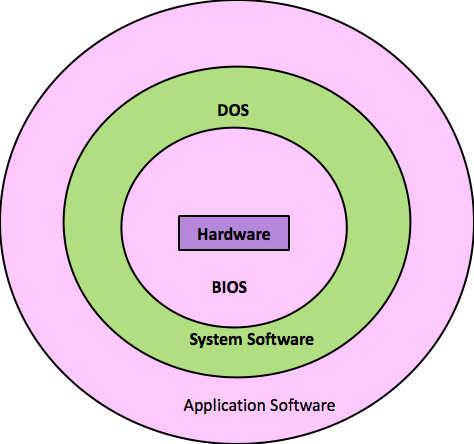
BIOS – Basic Input Output Control System DOS – Disk Operating System
Advanced System Concepts Location
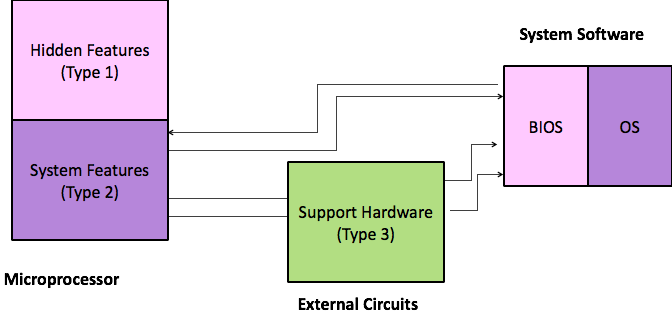
Operand Store
- μP puts mem address from internal register on to address bus
- μP puts data from one of internal registers onto data bus
- μP issues Memory write signal on control bus
- Memory takes contents on data bus & stores in given location
Data Bus
- Bidirection (from μP to memory & from memory to μP) – internal mechanism
- I/p & O/P to CPU & Memory
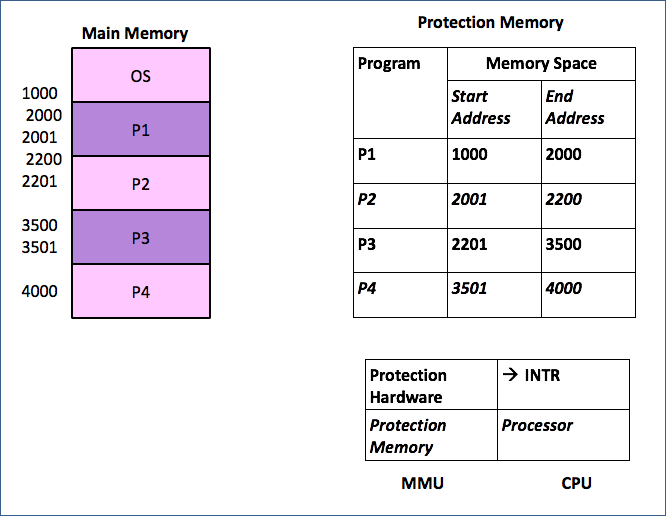
Memory Protection Mechanism