Advertisements
Multitasking and multiprogramming
UniProgramming
- CPU runs only one program at a time
- Program run one after other
- For given time only one program is loaded to memory
- CPU Idles
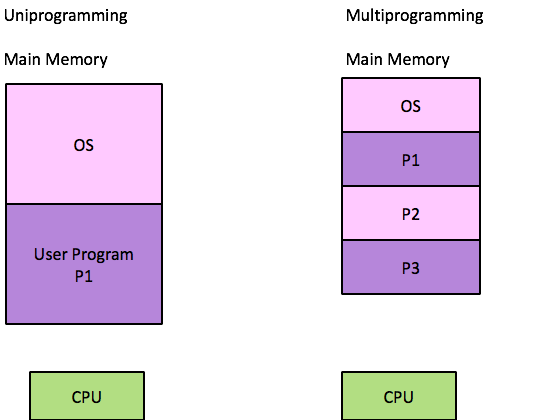
Multi Programming
- It runs multiple programs concurrently (but not simultaneously)
- One CPU switches between programs
- For given time, Many programs are present in main memory
- Eg: CPU – P1, Floppy read –P2, Hard disk write –P3, Print – P4.
- After P1’s completion CPU switch to another program based on priority
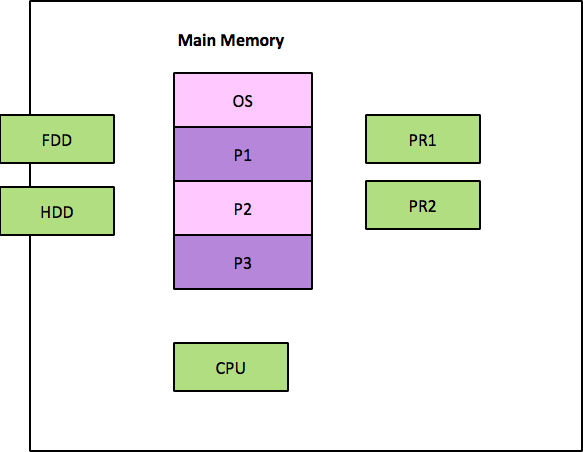
Achieve multiplexing
- High Throughput, Better utilization of CPU
- OS – dynamically allocate H/w resources & Memory for different Program
- Time taken for single program is more
- But total time to run many program is less
- Hardware has extra features used by OS
Eg:
CPU more sophisticated, memory protection & spl supervisory mode
Large size memory (since multiple program)
N-way Multiprogramming System
- System which supports concurrent running of N Programs
Memory Protection
protects from illegal memory access by other programs
Problems
- Corruption of program’s memory
- Use of another program’s data
Protection Hardware circuit used by OS.
Two types of Protection:
1. Write – only Protection
- By other programs, Reading is allowed & writing is denied.
- Overwriting into memory space of Pi is prevented.
- But Pi can be read from any location
2. Fetch – also protection
- Neither reading nor writing is allowed
- User can declare type of protection
Special Interrupt – protection violation interrupt
On violation, OS controls CPU and cancels that program
Supervisory mode Sees no program misuses or corrupts system files
2 modes in multi program
User Program mode
- Certain privileged instruction cant be executed. eg. I/O related instruction are privileged
b. Supervisory mode
- All instructions can be executed
- User program is run in User mode (CPU)
- When needs to perform I/O operations, OS calls special interrupt – Supervisory call
- In response, OS cares I/O & runs CPU in supervisory mode & then transfers control back to user
- Switching of mode done only by OS
Multiprogramming VS Multitasking
- Different tasks (Programs/Parts of program by single user / different user)
- Each task is independent routine
- Generally, same (as by computer system)
- Difference is Computer User.
- Hardware & OS does not differentiate between multitasking & multi program
Single User MultiProgram System (Batch Processing)
- Multiprogram system has only one terminal
- several users use system but they submit their Program to system operator/owner & collect results later
Multi user system
- If several users run program using separate terminals (window for communication with OS)
- Each user inputs his program from his terminal & get result on the terminal.
Time Sharing System
- Old concept not used now
- A central system (fast computer) with several terminals having resources shared by different users/terminal on time sharing basis.
- Time multiplexing concept is used for time sharing
- Time slice – rotation basis
- Response time is small but larger when servicing number of users
- OS should be sophisticated one.
Time sharing Vs. Multiprogramming system
- Time sharing similar to multiuser system but different from multitasking
- Runs for single user/terminal at given instant of time
- All system resources are available to user program currently being executed.
Multi user system – serves several program at given instant
- CPU executes one program & peripheral work for different program
- Time sharing system keeps scanning different terminals in fixed sequence & switches
- Multiuser system changes resource allocation only when I/O operation is completed or when a high priority program needs a resource currently used by low priority algorithm
