Advertisements
Microcomputer concepts
Microcomputer types
- Microcomputer designed around microprocessor
- Classified based on function/use & shape/size
Portable Computer
- Operate on battery
- Designed to consume low power
- Special Engineering & h/w design tech adopted to make it rugged and light weight
- Costlier and smaller in size
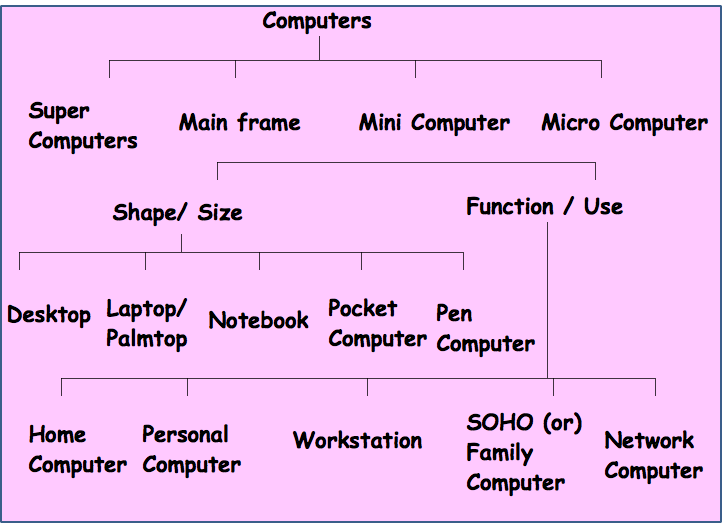
Functional Classification of Micro computer
1. Old Home Computer
- For simple Application
- Mainly for children education & game
- Now obsolete
2. Personal Computer (PC)
- Low cost general purpose micro computer
- Used for personal application by various profession
- Initial & maintenance cost – low
- No special provision like false flooring, false ceiling & air condition
3. Work station
- Special purpose micro computer for specific application such as CAD, DTP, Multimedia
- High performance & costlier
4. SOHO (Small office Home office)
- Modern home computer with all types of peripherals & s/w support
- Suits every one
5. Net Computer
- Supported by central server with hardware & software resources common to all
- Has minimum resources (CPU & Memory)
- Modern concept yet to be accepted by industry
Physical Classification of microcomputer
- Desktop (Table Top) – Horizontal & tower/vertical
- Laptop – can be kept on lap of user & is portable
- Notebook – Appears like notebook in shape & pportable
- Palmtop – fits on palm of user
- Pocket – like Pocket calculator
- Pen – looks like a pen
Operating System
- Provide support for configuring computer system, running programs, controlling I/O devices & user interaction
OS – collection of different program for performing functions like
- Handling user request for various services
- Scheduling of programs
- I/O operations
- Managing H/W units
Type of OS
- OS – small size stored in memory ROM or in Disk
- Modules – kernel (supervisor) scheduler, Process manager, File manager
- In real OS – Hybrid type
Types
- Batch OS – I/P & Program run one by one
- Interactive OS – I/P of data supported during program execution
- Time sharing OS – System shared by multiple users with terminals for interaction with OS
- Multitasking/ Multiprogramming OS – More than 1 task / program in memory. CPU switches between them
- Real time OS – OS periodically monitors various I/P according to different task
- Multiprocessors – Runs Many Processor simultaneously on many CPU in a single computer system.
