Advertisements
Memory Organization
Memory unit consists of
- Memory Address Register (MAR)
- Memory Data Register (MDR)
- Memory Control logic
- Memory Cells
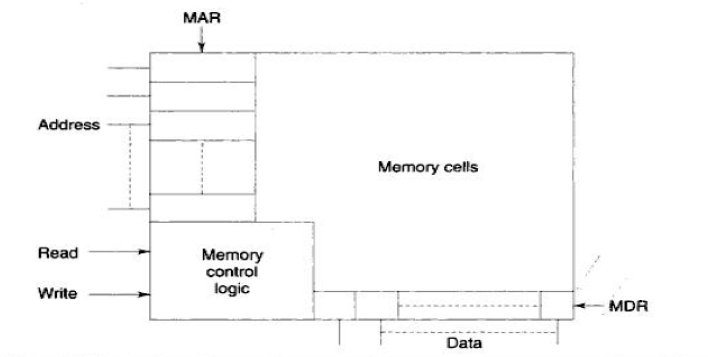
For Read Operation, CPU does
- Sends the address to MAR
- Send READ Signal to Memory Control Unit.
Memory – decodes address bits
- identifies location to be accessed
- initiates read operation of memory
- memory takes some amount of time to present contents of location in MDR.
- CPU transfers information from MDR
For write operation,
- Sends address to MAR
- Sends data to MDR
- Sends WRITE signal to memory control unit
- Decodes address & identifies location
- Routes MDR Content to memory &
- Initialize write operation
Memory Access time
|
Semi conductor Memory |
Order of 100ns |
|
Core memory |
Order of 800 ns |
During Read,
CPU takes information from MDR after the access time is over.
Memory Cycle Time:
- Memory access time + additional recovery time (since, busy with some internal operation)
- Minimum time interval necessary between two successive memory accesses.
- Memory access time & memory cycle time for both read & write.
Auxiliary memory:
Ware house for storing several program & data
- Floppy disk drive
- Hard disk drive
- Magnetic tape drive
- CD-ROM (Compact Disc – Read only memory)
