Advertisements
Interrupts
- To react to special / urgent situation.
- To suspend current program’s execution temporarily to do some other program.
- Convenient time to suspend current program is, when CPU executes 1 instruction & is about to start fetching next instruction
- Cause: H/w or S/w ( error, unexpected conditions, external service req)
Eg: On Power fail Interrupt, Save CPU Status in backup memory
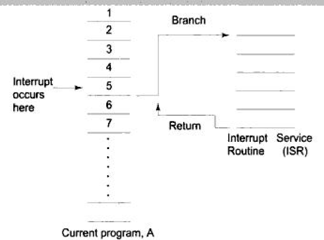
- CPU recognizes b4 5th inst fetch
- Suspends current prog exe
- Branches to ISR
- Aft ISR, CPU returns to interruped Prog & fectch Inst.
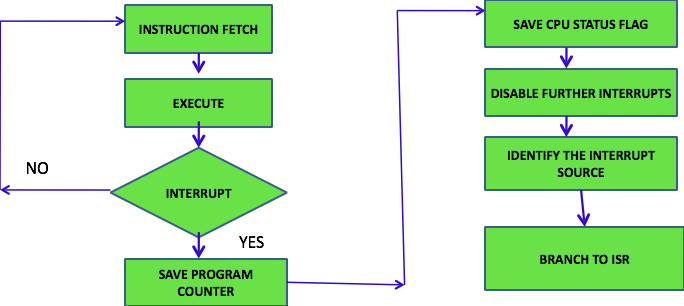
What happens when interrupt occurs:
- Before CPU, switches from current program to ISR.
- CPU saves content of IAC & PSW. (to cont current prog aft ISR)
- Load start address of ISR into IAC
- CPU starts executing ISR. Interrupt Service Sequence
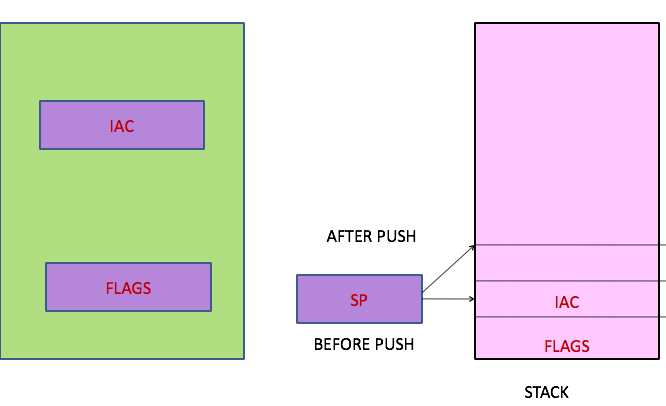
Nested Interrupts & Stack
- Interrupt to an Interrupt–CPU switch from current ISR to new ISR
- So, store more than one (IAC&PSW)
- Stack Mechanism to store (IAC &PSW)
Interrupt Priority
- To service more simultaneous Interrupt
- Hardware priority Controller/Encoder Circuit in CPU.
- One highest priority & rest different order of priorities
- Priority Encoder identifies high priority interrupt among present interrupts – CPU switch to ISR – other pending till chance
Interrupt Disabling & Masking
- Execute set of instruction without interruption – Disable by s/w
- Reset IE flag till your completion
Masking Interrupts
- Disable selective interrupts – masked bits to Priority Controller
- Ignores those interrupts till masking is removed.
Non maskable interrupt (NMI)
- Emergency interrupts – servicing should not be delayed
- Occur anytime (IE is 0 or 1)
- Cannot be masked by any programs
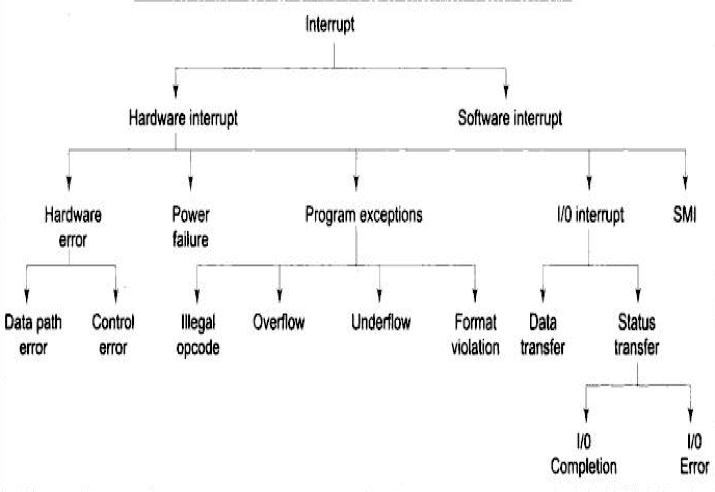
Types
- Power fail interrupt
- Hardware Error
System Management Interrupt (SMI)
- Special purpose interrupt taking action to minimise power consumption
