Advertisements
Input Ouput Techniques
Data Transfer -> moving some no. of bytes from i/p device to Memory or Memory to o/p device
Technique of data transfer
- Programmed mode
- Interrupt mode
- DMA Mode
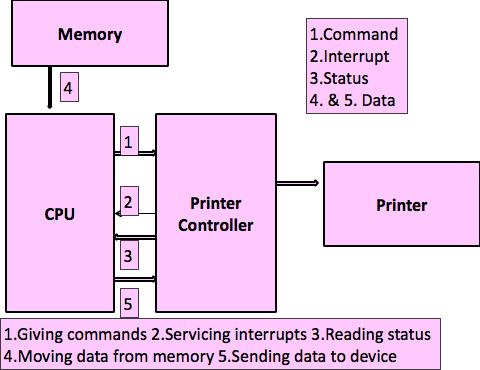
Programmed Mode/ Polling
- Incharge of Data transfer->CPU
- It first transfers data byte from memory to CPU & then to the device
- These actions are done for every byte of data with appropriate instructions in program
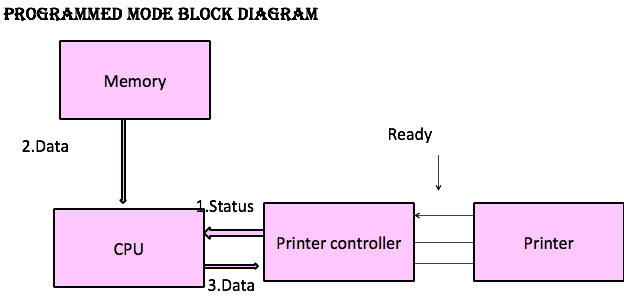
- Reading device status
- Moving data from memory
- Sending data to device
Programmed Mode of data transfer
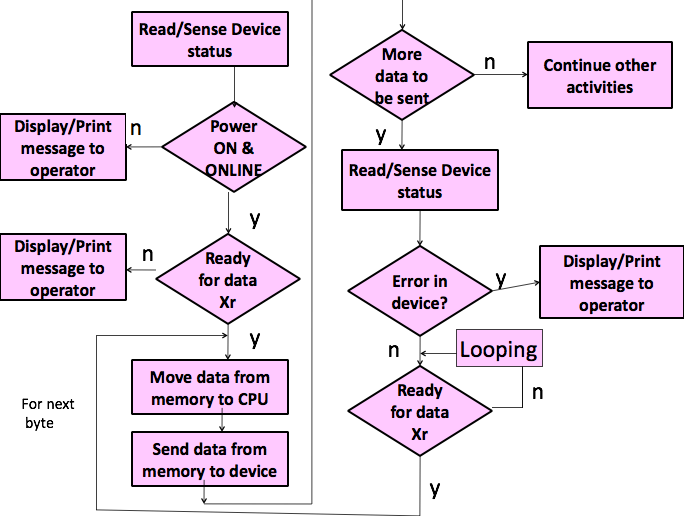
Functions to be performed by program for i/p device are:
- Checking wtr device powered ON
- Reading device status
- Checking if the device is ready
- Reading data from device
- Storing data in memory
- Checking wtr device is ready with next byte of data transfer
- If ready, repeat st 4 to 6.
- If not ready, loop on st 6.
Note:
- CPU is totally dedicated in data transfer.
- CPU time is wasted for slow I/O device.
- Similar operations for o/device except the direction of data transfer
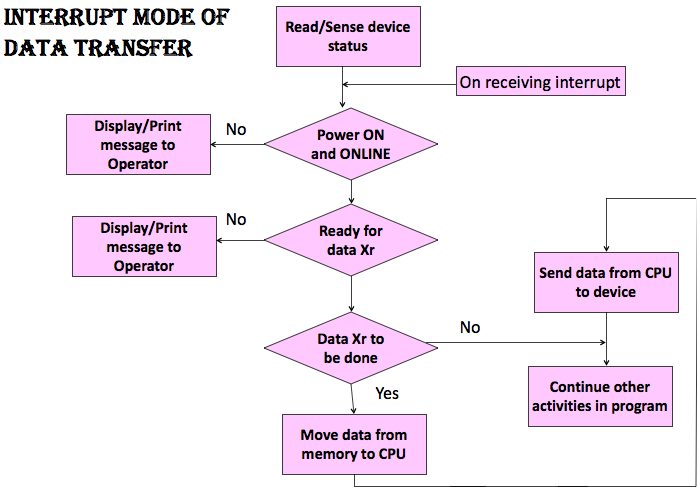
Interrupt Mode
- CPU does the data transfer.
- But skips the task of checking wtr device is ready with data byte in case of an input device
- CPU is free till the device is ready with next byte
- & hence can execute non- I/O program execution.
- Program organized into I/o (is ISR) & non-I/O routines.
- CPU not tied up with unproductive operations
- Utilized better.
Interrupt Mode Block Diagram
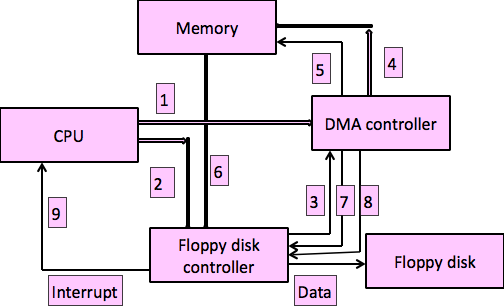
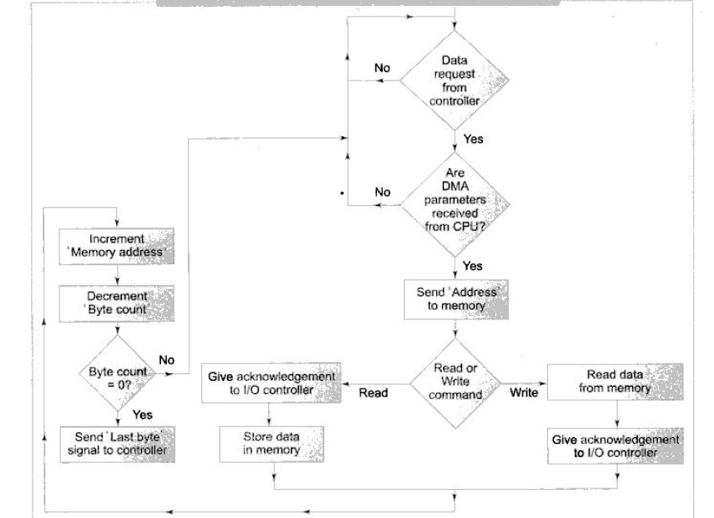
 DMA Mode
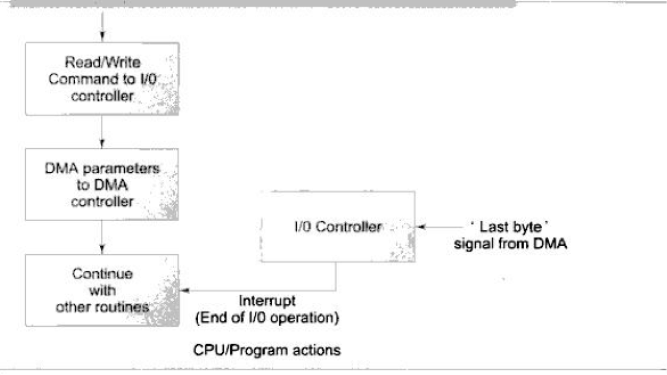
DMA Mode
- CPU does not perform data transfer.
- DMA controller does data transfer.
- CPU only supplies DMA parameters to the DMA Controller.
Parameters are
- Start address : Memory address from where data transfer has to be started
- Byte count: Number of data bytes to be transferred
- Direction: Direction of data transfer
- Device: I/O device to be involved in data transfer
Program must give appropriate R/W command to device controller
Dma mode of data transfer (a)
DMA mode block diagram