Advertisements
Hard Disk Drive
- Effective I/O device – Secondary/auxiliary memory
- Components
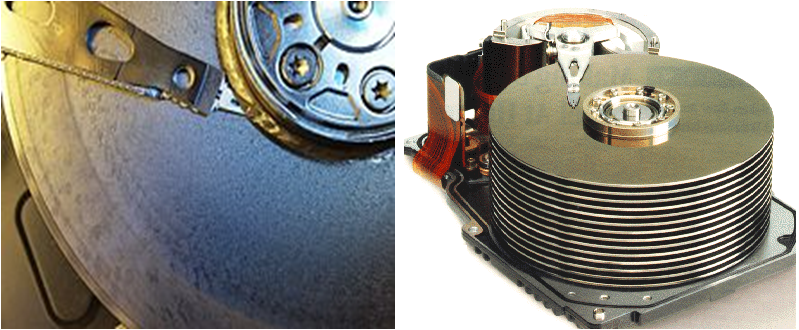
- One or more platters on disks mounted with common spindle
- Platter has 2 magnetic surface – top & bottom
- Oxide coating on aluminum disk surface & currently thin film disks affixed to substrate
- R/W head flies over disk
- Earlier ferrite heads & now thin film heads
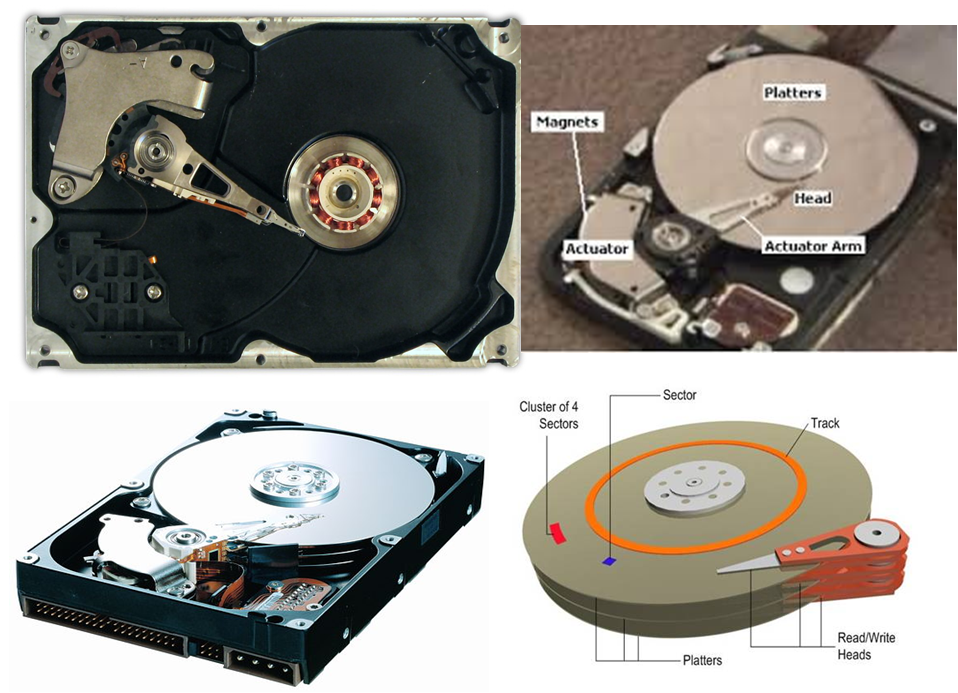
Working
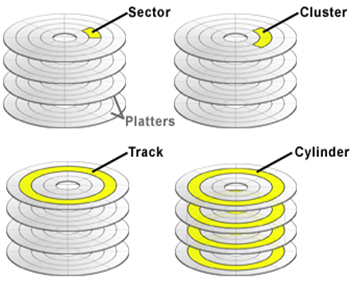
- Data recorded on tracks
- Cylinders – tracks on a specific circle
- No. of cylinders = no. of tracks in a surface
- Data – MFM form & serial through singe wire (DATA + CLOCK)
- Control signals inform exact location of storage
- Cylinder number, surface number, etc.
- Disk rotation: 2400, 4800, 7200 rpm

Types I
1. Removable Disk Drive
- Disks can be removed when not used
- So, Any number of disk packs
- Transfer of data from one disk to another
2. Fixed Disk Drive
- Disk cannot be removed from disk drive
Types II
1. Single head assembly Drive
- One head for each surface
- Heads mounted on one spindle & move together
- All head positioned in same cylinder
2. Dual head assembly Drive
- Two heads for each surface
- One set covers 1st half & 2nd set covers 2nd half of cylinder
Types III
1. Winchester Disk Drive
- R/W heads in a sealed enclosure
- Head flies close to hard disk less than 19 micro inches
- heads park on parking / landing zone – no data written
- Surface of disk is lubricated – prevent damage to head or track
- Higher track densities
- No preventive maintenance
- Built-in preventive system against head crash – back up
2. Non – winchester Disk Drive
- Obsolete
- used till 1973
Types IV
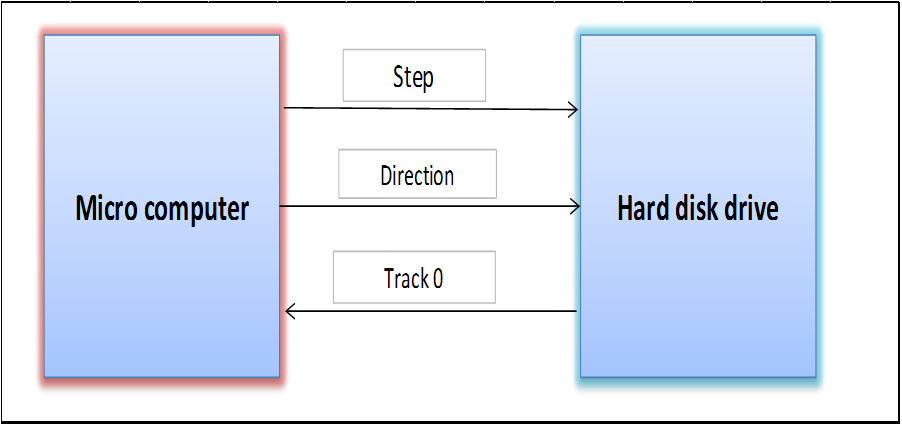
1. Open loop Disk Drive
- Stepper motor for head movement
- Track-0 is reference point
- STEP Pulse issued to stepper motor for head move on track
- No. of step pulses decide total distance of head movement
- No feed back system to verify head movement
- S/w tracks formatting info to verify head correctness
- Direction signal – direction of movement of stepper motor (forward & backward)
- When head is on track0, HDD sends TRACK0
- Present track number is with ref to track0 & Low cost
Open loop Disk Drive
Closed loop disk drive
- Hard disk info – reference info positioning
Ways for storing head positioning information
- Servo tracks
- Servo surface
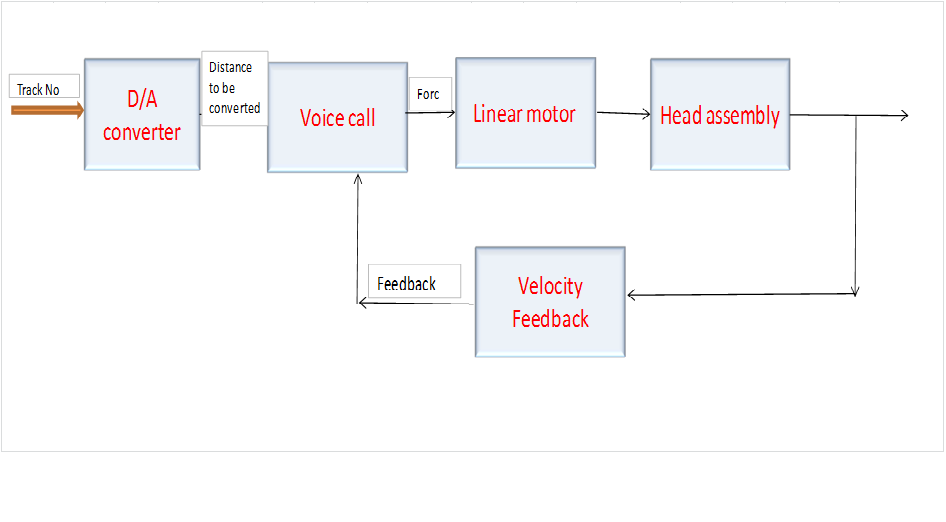
- Linear voice coil mechanism – control linear motor position using feedback control – moves head at different velocities
- Head acceleration based on distance
- Automatic reposition
Closed loop positioning system
Advantage
- Accurate head positioning on desired track
- Less access time
- Cost twice or thrice of open loop system
- Suitable for high performance system
Size & capacity
- Inches – platters diameter
- Sizes – 20, 14, 101/2, 8, 51/4, 31/2, 21/2 inches
- Capacity – size & technology
- 14 inch HDD – 20MB & 21/2 inch HDD – 40GB
To have more data capacity,
- Higher track density
- Higher recording density
- Better Packaging methods
Hard disk drive organization
- Both electronic & electromechanical subsystems, viz.,
- R/W Head
- Disks
- Spindle motor
- Positioning mechanism
- Air Circulation System
- Air Filters
- In Winchester HD – sealed head disk assembly (HAD) with R/W head, disks, band actuator assembly & air circulation system
Head Types
- Manganese/Zinc ferrite head
- Thin film head
Standard interface for hard disk connection
- SMD, IDE, EIDE, SCSI, IPI, ESDI, ST506/412
- In ST506/412 interface,
- Radial/Data Cable - Data Sent/received on separate cable
Daisy Chain Cable
- Control sgls sent through to 1st HDD
- Same sgls extended to 2nd HDD by another cable
Data organization on hard disk
- Magnetic tracks – into sectors
- Currently, Soft sector format
- In ID Field,
- Track Number
- Head Number
- Sector Number
